Memory Game Maker

Image courtesy of Google Images
Link: http://www.education.vic.gov.au/languagesonline/games/memory/index.htm
Year Level: 3 – 6
Description:
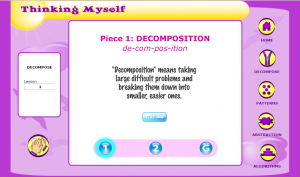
Memory Game Maker allows students and teachers to create and interactive memory games using text, images, symbols or audio related to the subject or topic they’re learning about to share with others. Students can customise their games visual features as well so that it is unique. Students can upload their creation online or store in a folder or share with other students/ teachers. This program allows students to create a game that can be adapted for all students learning needs and abilities. This program can be used in mathematics, English, music, LOTE and science as a tool of learning, assessing and revising content in these learning areas in a fun. Interactive and engaging way. This program can be downloaded onto any IOS products such as Ipads also android and windows so it can be accessed and downloaded on any device that the school has.
Strand: Digital Technology
Sub Strands: Knowledge and Understanding & Process and Production Skills
Year: 3-4
Content Descriptor:
Explore and use a range of digital systems with peripheral devices for different purposes, and transmit different types of data (ACTDIK007)
Recognise different types of data and explore how the same data can be represented in different ways (ACTDIK008)
Skills:
Collect, access and present different types of data using simple software to create information and solve problems (ACTDIP009)
Define simple problems, and describe and follow a sequence of steps and decisions (algorithms) needed to solve them (ACTDIP010)
Implement simple digital solutions as visual programs with algorithms involving branching (decisions) and user input (ACTDIP011)
Explain how developed solutions and existing information systems meet common personal, school or community needs, and envisage new ways of using them (ACTDIP012)
Work with others to plan the creation and communication of ideas and information safely, applying agreed ethical and social protocols(ACTDIP013)
General Capabilities:
Literacy
Numeracy
Technology Capability
Critical and Creative Thinking
Year 5-6:
Content Descriptor:
Knowledge and Understanding
Investigate the main components of common digital systems, their basic functions and interactions, and how such digital systems may connect together to form networks to transmit data (ACTDIK014)
Skills:
Design a user interface for a digital system, generating and considering alternative designs (ACTDIP018)
Design, modify and follow simple algorithms represented diagrammatically and in English involving sequences of steps, branching, and iteration(repetition) (ACTDIP019)
Implement digital solutions as simple visual programs involving branching, iteration (repetition), and user input (ACTDIP020)
Explain how developed solutions and existing information systems are sustainable and meet local community needs, considering opportunities and consequences for future applications (ACTDIP021)
Manage the creation and communication of ideas and information including online collaborative projects, applying agreed ethical, social and technical protocols (ACTDIP022)
General Capabilities:
Literacy
Numeracy
Technology Capability
Critical and Creative Thinking
Personal and Social Capability
Ethical Understanding
Links to Other Learning Areas:
English
Maths
History
LOTE
Music
Year 5; 6
Learning Area: English – Language
Content descriptions
Explain sequences of images in print texts and compare these to the ways hyperlinked digital texts are organised, explaining their effect on viewers’ interpretations (ACELA1511)
Elaborations
Interpreting narrative texts told as wordless picture books
Identifying and comparing sequences of images revealed through different hyperlink choices
General capabilities
Literacy
Critical and creative thinking
ICT competence
Learning Area: English – Literacy
Content descriptions
Use a range of software including word processing programs with fluency to construct, edit and publish written text, and select, edit and place visual, print and audio elements (ACELY1707)
Elaborations
Writing letters in print and by email, composing with increasing fluency, accuracy and legibility and demonstrating understanding of what the audience may want to hear
General capabilities
Literacy
ICT competence
Learning Area: English – Literacy
Content descriptions
Use a range of software, including word processing programs, learning new functions as required to create texts (ACELY1717)
Elaborations
Selecting and combining software functions as needed to create texts
General capabilities
ICT competence
Skills from LOTE
Revise a wide variety of linguistic and cultural concepts.
Actively using the language in an educational way.