Strand
: Design and Technology
Sub-strand: Design and technologies process and production skills
Bands: 3 to 7
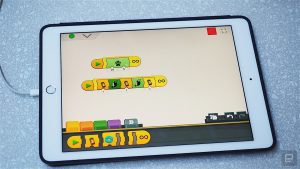
Boost is Lego’s latest introduction of Lego robotics to 2017. Boost is a step up from Lego’s Mindstorms and WeDo 2.0 robotics kits, introducing movement to Lego. Boost gives students the opportunity to engage in the active learning process, whereby students construct their own learning. Boost is not only fun, but it’s also educational. Using the software available on the Lego Boost website, teachers can tailor learning experiences which are relevant, hands on and fun, while learning the fundamentals of coding and computational thinking.
How?
Boost has over 60 different coding activities available. Teachers can select the activity they would like to incorporate into their learning experience from the Boost App, available for most Android and Apple devices. Coding with Lego is easy, students demonstrate their problem solving skills and ability to think critically by programming their Lego Boost creation to suit the learning task. Boost Lego has special bricks including a motor and sensors, which gauge surrounding colours and distance from objects in its path.
LEGO Boost isn’t available until August 2017, however children and adults are bursting to try this new technology!
Content Descriptors
Year 3 to Year 4
- Generate, develop, and communicate design ideas and decisions using appropriate technical terms and graphical representation techniques (ACTDEP015)
- Select and use materials, components, tools, equipment and techniques and use safe work practices to make designed solutions (ACTDEP016)
- Plan a sequence of production steps when making designed solutions individually and collaboratively (ACTDEP018)
Year 5 to Year 6
- Generate, develop and communicate design ideas and processes for audiences using appropriate technical terms and graphical representation techniques (ACTDEP025)
- Select appropriate materials, components, tools, equipment and techniques and apply safe procedures to make designed solutions (ACTDEP026)
- Develop project plans that include consideration of resources when making designed solutions individually and collaboratively (ACTDEP028)
Year 7 to Year 8
- Critique needs or opportunities for designing and investigate, analyse and select from a range of materials, components, tools, equipment and processes to develop design ideas (ACTDEP035)
- Select and justify choices of materials, components, tools, equipment and techniques to effectively and safely make designed solutions (ACTDEP037)
- Use project management processes when working individually and collaboratively to coordinate production of designed solutions (ACTDEP039
General capabilities
- Literacy
- Numeracy
- Science
- Critical Thinking and Creative Thinking
- Personal and Social capability
- Information and Communication Technology
Further Information
Youtube – Boost LEGO in Education
Youtube – WeDo LEGO in Education
Lego Computer Coding Activities
By Emily Richardson